30. April 2025 By Dr. Louis Schäfer
Planning reimagined: How AI simplifies production planning
The digitisation and automation of production continue to advance. Modern smart factories are packed with intelligent robots, networked machines and data-driven decisions. But the planning of such systems is lagging behind this progress. While generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) has been revolutionising our everyday lives since the introduction of ChatGPT in November 2022, production system planning is still largely manual and document-based.
An insightful example: Large automotive OEMs sometimes use over 150 different planning tools – a complex, often inefficient network with one goal: to derive a production system for manufacturing and assembling the product based on a parts list from engineering. Despite the multitude of tools, the degree of automation remains low in most cases, and planning is one of the most R&D-intensive tasks there is. But what exactly does production planning look like at present – and what steps are necessary to make AI-supported planning a reality?
The current planning process – lots of manual work, little automation
The planning process in production is a complex interplay of different tools and manually created schedules. Typically, a new production line is planned directly on the basis of the parts list. This means that the work steps for manufacturing and assembling the product are usually derived manually from the parts lists. This planning also includes the assignment of work steps to production stations and their sequence.
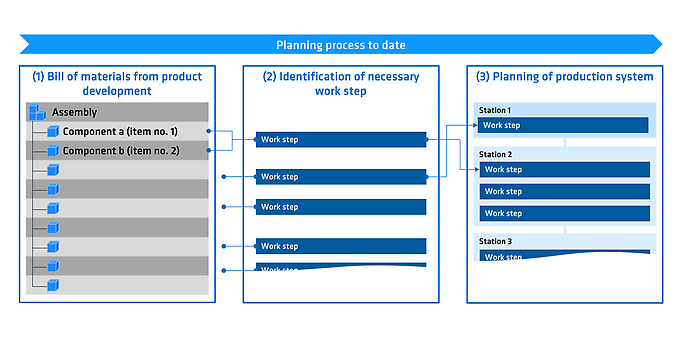
The problem: Every new line is planned from scratch, even though similar or even identical production processes often existed in previous projects. Instead of systematically utilising this knowledge, planning remains a time-consuming process in many companies.
To overcome these challenges, the introduction of a maximum priority graph is recommended. This enables recurring sequence restrictions to be systematically derived from historical planning data and standardised. In this way, resource-independent processes can be automatically identified and efficiently integrated into the resource-related planning of new production lines. This not only saves time and resources, but also increases planning reliability and consistency.
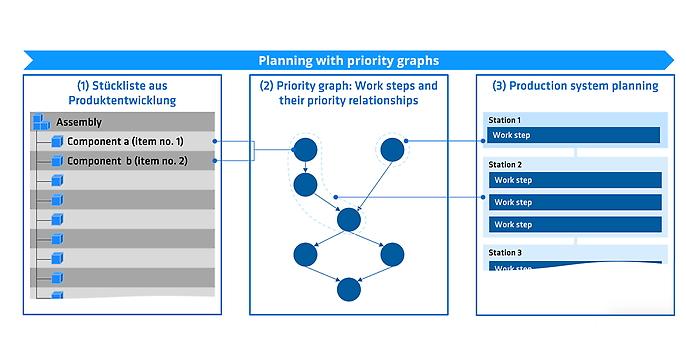
But how can such a priority graph be created when industrial planning quickly involves more than 10,000 different work steps?
Future-proof production starts digitally
adesso supports companies in the manufacturing industry in making their production smarter, more connected and more efficient. From IoT platforms and data integration to AI-based processes, we bring digitalisation to your manufacturing.
Der Maximal-Vorranggraph – Wie KI und GenAI die Planung automatisieren
Diese unüberblickbare Menge an Arbeitsschritten erfordert eine Automatisierung des Planungsprozesses. Der Einsatz von KI bietet eine Chance, diese Problematik grundlegend zu lösen. Die Idee des Maximal-Vorranggraphen ist es, die Arbeitsschritte aus verschiedenen Planungen zu analysieren und dabei gemeinsame Muster zu erkennen. Wie das funktioniert, wird im Folgenden kurz erläutert:
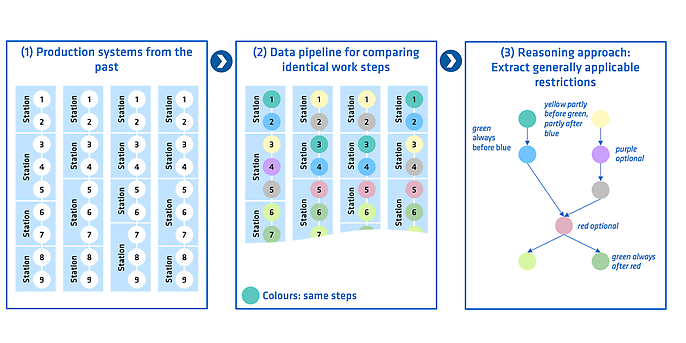
- 1. Data extraction, cleansing and structuring:
- Historical planning data from ERP systems and planning tools is collected, cleansed (e.g. by harmonising the designations of work steps using named entity recognition) and then transferred to a uniform structure, with each data record mapping the sequence of work steps on a production line.
- 2. Pattern recognition and sequence analysis:
- 1. Using recurrent neural networks (RNN) or long short-term memory (LSTM) to recognise probable sequence patterns.
- 2. Using graph neural networks (GNNs) to model the work steps as nodes and their sequence as edges to detect frequently recurring paths or, more simply, with a fixed number of nodes using the adjacency matrix and convolutional neural networks (CNNs).
- 3. Association analysis (Apriori/FP-Growth) to identify pairs of work steps that always occur one after the other.
- 3. Creation of the maximum priority graph to aggregate the identified priority relationships into a consistent graph:
- 1. Graph generation with work steps as nodes and priority relationships as directed edges.
- 2. Consistency check to ensure that there are no cycles.
- 3. Graph optimisation to remove redundant edges that can be derived transitively.
- 4. Use of GenAI to improve and generalise the priority graph:
- 1. Use large language models (LLMs) to generate alternative work step sequences that take technological sequence restrictions into account.
- 2. Statistical anomaly detection to identify unusual (i.e., rare) sequences and suggest alternatives.
- 3. Identification of critical priority relationships and query about their necessity (technical priority relationship or ‘I've always done it this way’) in an interactive chatbot.
- 5. Validation and verification to ensure the quality and consistency of the priority graph by comparing it with expert planning.
- 6. Implementation and integration into the existing tool landscape via standard interfaces (JSON, CSV, etc.), including continuous learning through user feedback.
This approach not only makes production planning faster and more standardised, but also more robust and adaptive. As new planning data becomes available, AI can continuously update and optimise the graph. This saves time and money in one of the most R&D-intensive planning tasks.
Call to action – act now before you lose touch
Manufacturing companies are faced with the challenge of automating production planning while reducing complexity. To avoid falling behind, adesso recommends the following steps:
- 1. Consolidate data: Create a central database from historical planning data.
- 2. Build AI infrastructure: Invest in AI technologies that are specifically designed to analyse production data.
- 3. Recognise patterns: Use AI to identify recurring work sequences.
- 4. Enable integration: Embed the priority graph in your planning tools.
- 5. Conduct training: Equip your team with the knowledge to use GenAI efficiently in planning.
The course for automated production planning must be set now. Companies that embrace AI-supported planning early on will secure decisive competitive advantages – whether through faster planning, fewer errors or the flexible consideration of new requirements.
We support you!
Want to finally make your production planning fit for the future? We show you how to create real added value with AI and GenAI – from data consolidation to seamless integration of the maximum priority graph.

