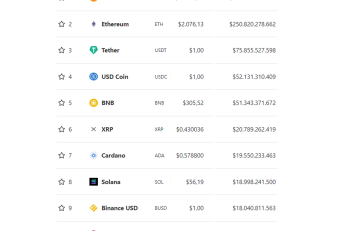
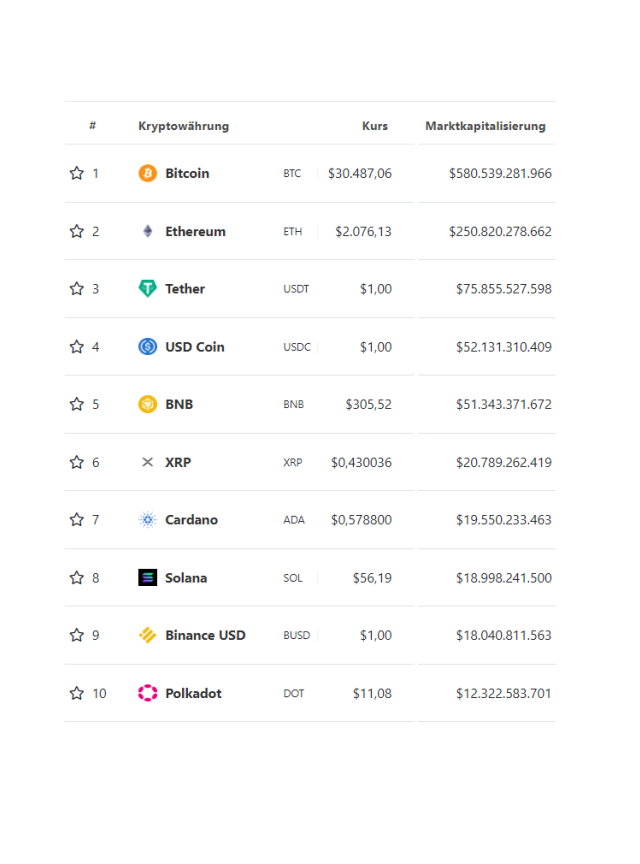
Altcoin
Altcoin is an abbreviation of ‘alternative coin’ and is an umbrella term for all cryptocurrencies except Bitcoin.
Bitcoin
Bitcoin is the first cryptocurrency created on blockchain technology. Two people can send bitcoins to each other independently of a bank or a state institution. Each Bitcoin transaction is registered in the blockchain, analogous to a bank's ledger. Bitcoin is the most popular cryptocurrency today.
Blockchain
Blockchain technology enables data to be stored in blocks, which are cryptographically sealed. When a block is full, a new block is created. The blocks are merged to form a chain of blocks. In the process, the preceding block has information from the previous block (hash). This makes the blockchain safe from manipulation, as in order to manipulate a blockchain, every single block would have to be manipulated.
Decentralised applications (dapps)
Decentralised applications do not function on a central instance, but in a network of machines. Important data and states of an application are stored decentrally, but the code is often managed and stored on a regular server.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi)
Decentralised financial service describes an open and efficient financial system based on the blockchain that is organised outside the existing infrastructure. It aims to create access to any form of financial service needed available to all people around the world. There is no need for banks or authority to act as intermediaries, making this financial ecosystem presumably transparent, fair, frictionless, and costeffective.
Digital Assets
Digital assets are an electronic image of physical assets, which regulate the ownership or share by means of tokens. They are managed via the blockchain or a distributed ledger.
Digital Wallet
Digital assets are stored securely in digital wallets.
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
Central bank digital currency refers to projects that contain a digital currency issued by a central bank and whose exchange rate is 1:1 that of the represented national currency.
According to a survey in 2021, around 80% of central banks worldwide are investigating CBDCs.
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT)
A DLT system is a digital database. Data or information is stored on computers that are distributed across different locations (decentralised).
What is the difference between blockchain and distributed ledger technology (DLT)? You can compare this with computer vs. smartphone. Every smartphone is somehow also a computer, but a computer does not correspond to a smartphone. In other words, the blockchain is a type of distributed ledger technology that has common functions with DLT, but also has just as many differences. The main difference lies in the way information is stored, such as the sequence, the consensus algorithms, the type of transaction validations or the underlying structure of both technologies.
Ethereum
Based on blockchain technology, Ethereum enables the creation and execution of smart contracts and decentralised applications (dapps). Third parties are no longer necessary.
ETP
ETP stands for Exchange Traded Products and is the umbrella term for:
- ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds: track an index, industry, or theme)
- ETCs (Exchange Traded Commodities: for investing in commodities and precious metals)
- ETNs (Exchange Traded Notes: for investment currencies).
ETPs are passively managed and are securities tradable on the stock exchange.
ETPs with crypto investments are already offered today. They offer institutional clients a new asset class with risk diversification.
Fiat currency
Fiat currencies are the cash currencies issued by national banks, such as the CHF, EUR, USD etc.
Hash
In blockchain technology, a hash is a digital fingerprint of a block and therefore a fundamental building component thereof. Hashing, the conversion of a string of characters into a numeric value, is used to index and retrieve database elements.
Crypto exchange
A crypto exchange is a digital marketplace where cryptocurrencies and other digital assets can be traded.
Cryptography
This is a method of transmitting data in encrypted form so that only the recipient can read (decrypt) this data.